- August 23, 2025
- Our Blog, Our Latest News, Projects, Uncategorized
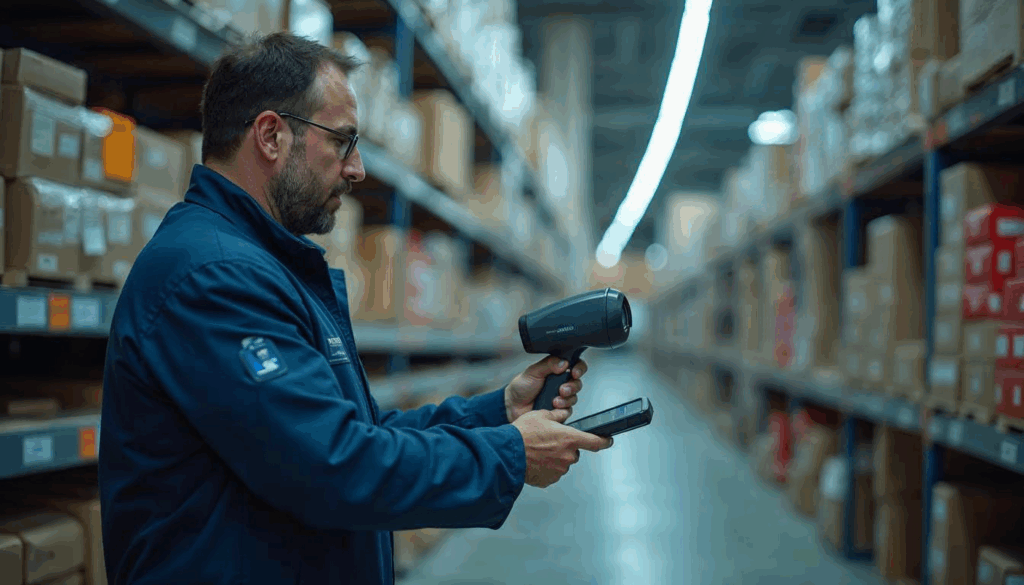

What is Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC)
AIDC is the broad term for technologies with the capabilities to automatic collection, storage, and categorization of data without manual input, primarily used for identification, validation, asset tracking, and system integration in various industries.
AIDC combines both hardware and software to streamline processes involving the collection and management of data. Doing so significantly reduces human error, improve efficiency of processes thereby saving time and costs. Having these data allow businesses to collect data, business analytics and gain business insights.
As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, understanding the capabilities, applications, and potential of AIDC becomes crucial for staying competitive in today’s fast-paced business environment. This article delves into the intricacies of AIDC, exploring its key components, diverse applications, and the transformative impact it has on modern business operations.
How it works
The deployment of AIDC capabilities may differ depending on the sector and operational needs. These processes usually make involves
- Data and Data Encoding: Data carries (such as labels and tags) are encoded with alphanumeric characters data. It is also possible that the data to be collected need not be encoded, this can come in the form of image or sound.
- Machine Reading or Scanning: Specialized devices are used to read the encoded data.
- Data Decoding: With the help of a transducer, the information collected are then translated back into digital data for storage or further processing, usually through an integrated software.
AIDC covers a wide scope, the technology is mostly used for one of three things:
- Identification and validation
- asset tracking, and
- interfaces to other systems.
Common AIDC Technologies and its applications
Barcode and QR Code Readers – AIDC has been utilized for years through barcode labels and reader technologies. Barcodes serve various purposes, such as tracking, identification, and inventory management across industries including retail, e-commerce, healthcare, education, manufacturing, entertainment, and more.
RFID – RFID tags transmit detailed information to a scanner, which is captured by a specialized reader through AIDC. These tags are typically used on items that require advanced tracking or real-time data collection and reporting.
Biometrics – Biometrics identify individuals by comparing biological features like fingerprints or irises using a specialized AIDC scanning process. Once confined to science fiction, this advanced technology is now widely used in offices and personal mobile devices.
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) – OCR uses AIDC to scan and interpret written or printed text. It is a crucial technology in the digitization of documents and other text-based materials.
Magnetic Strips – Magnetic strips employ AIDC technology for quick information verification via “swiping.” This technology is commonly found on items such as credit/debit cards, building access cards, library cards, and public transit passes.
Smart Cards – Smart cards are an advanced form of magnetic strips, used similarly but often for personal applications. They also utilize AIDC technology and are commonly found in passports.
Voice Recognition – Similar to biometrics, voice recognition captures and analyzes voice data using AIDC technology to match it against a database of voice samples for identification.
Bluetooth Low-Energy (BLE) – As innovation advances and operational needs increases, the use cases for BLE have been growing in recent years. By working together with sensors (e.g. heartbeat, movement), it provides new datasets driving operation capabilities. Healthcare is one sector that has seen greater innovations in the use of BLE.
AIDC has become a crucial tool in sectors such as retail, manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics management, driving improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and productivity.
The Challenges of Using Automatic Identification and Data Capture
Given that many of the technologies mentioned involve the collection and storage of data, some of which may be sensitive, concerns about theft, fraud, and data breaches are always present.
Let’s focus specifically on RFID in relation to Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC). While RFID tags can store a significant amount of information, this data is not always secure. Since RFID operates using radio waves, it is vulnerable to hacking, which means that sensitive information could be accessed by anyone capable of intercepting the signals.
Moreover, although AIDC technologies continue to advance rapidly, they are not yet flawless. There isn’t always a perfectly seamless system in place, which can result in occasional malfunctions. Fortunately, there is a wide array of products utilizing AIDC technologies to help address these challenges.
Final Thoughts on AIDC
Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC) technologies have transformed data management across various industries, bringing substantial improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and real-time visibility. From barcodes to biometrics, AIDC systems automate data collection and processing, minimizing human error and conserving valuable time and resources.
As technology evolves, AIDC’s impact on innovation and operational performance continues to expand. Its integration with emerging technologies such as AI and IoT holds immense potential for enhancing data-driven decision-making and optimizing processes. For businesses striving to remain competitive in an increasingly digital world, adopting AIDC is not just advantageous—it’s critical.
Ultimately, Automatic Identification and Data Capture offers a transformative toolkit that streamlines operations, boosts productivity, and enhances customer satisfaction. Looking ahead, the ongoing development and widespread adoption of AIDC will undoubtedly be pivotal in shaping business operations across all industries.