RFID
Are manual processes slowing you down? Inaccurate inventory, data entry errors, and security risks can create major challenges for any business. It’s time to leave outdated tracking methods behind and step into a more efficient future.
Our RFID technology uses radio waves to automate your entire system. Scan multiple items at once without a direct line of sight, gaining real-time visibility and control. Boost productivity, enhance security, and eliminate losses with a smarter way to track your assets.
Features of RFID Solution
High-Precision Inventory Management
RFID technology boosts inventory accuracy to nearly 99% by automating data capture. This cuts down on manual counting errors, helps prevent stockouts, and lets you know exactly what you have on hand at all times.
Boosted Operational Efficiency
By automating tasks like receiving and shipping, RFID makes your entire workflow smoother and faster. Its ability to scan multiple items at once, even through boxes, significantly reduces manual labor and speeds up operations.
Real-Time Supply Chain Visibility
Get a complete, live view of your products and assets from start to finish. This end-to-end tracking gives you unparalleled control over your supply chain, helping to optimize logistics and make quick, informed decisions.
Significant Cost Reduction
RFID saves money by cutting labor costs, reducing errors, and preventing product loss or theft. It also optimizes how you use your valuable assets, often leading to a quick return on your investment and higher profits.
Improved Quality Control
Track items through every step of production with RFID. This helps you catch defects early and maintain a complete history of each product, ensuring top-notch quality and making it easy to meet regulatory requirements.
Enhanced Security and Loss Prevention
Each RFID tag has a unique ID, making it easy to spot fakes and prevent counterfeiting. This feature also provides excellent anti-theft protection by alerting you when items are moved without authorization.
Superior Data for Smarter Decisions
The system gathers tons of real-time data about your operations. Analyzing this information helps you spot trends, improve processes, and make smarter strategic decisions to grow your business and keep customers happy.
How Does RFID Solution Works
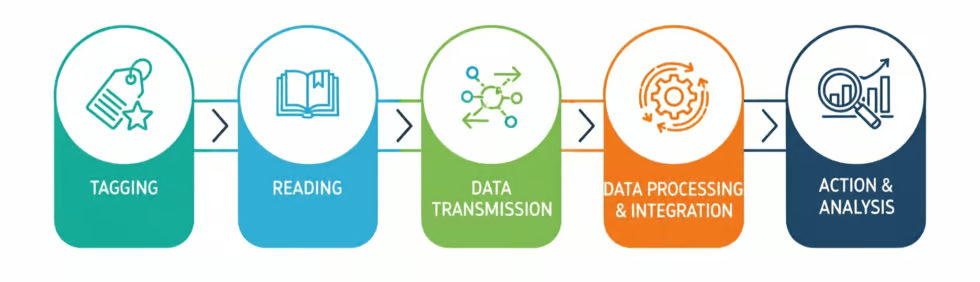
Implementation of RFID Solution
-
1. Discovery & AssessmentFirst, define your objectives and conduct a feasibility study to assess your infrastructure and potential signal interferences. Audit your current software systems to determine integration needs and assemble a cross-functional project team from IT, operations, and management to guide the project from the start.
-
2. Solution Design & PlanningSelect the appropriate RFID tags and plan the optimal placement for readers and antennas to ensure complete coverage. Design the necessary network and software architecture for seamless data flow, and create a detailed project timeline with clear milestones and a comprehensive budget to keep everything on track.
-
3. Procurement & InstallationBegin by purchasing all required hardware, including RFID tags, readers, antennas, and printers. Next, install the network cabling and mount the readers and antennas according to your design plan. The final step is to apply the RFID tags to all your inventory, assets, or products consistently.
-
4. Testing & Optimization (Pilot Phase)Implement the solution in a small, controlled pilot program to test functionality and identify any issues early. Verify data accuracy, validate the impact on workflows, and gather feedback from users to troubleshoot and refine the system before a full-scale deployment.
-
5. Training & RolloutThoroughly train all relevant personnel, including warehouse staff and IT teams, on how to use the new RFID system. Based on the pilot's success, gradually expand the implementation across your business in phases. Establish clear channels for ongoing technical support and maintenance to ensure smooth operation.
-
6. Monitoring & Continuous ImprovementContinuously monitor the system’s performance, read rates, and data accuracy to maintain reliability. Conduct periodic audits to optimize reader placements and software configurations. Use the data generated by the system for reporting and analytics to drive continuous process improvement and strategic decision-making.

Barcode vs RFID
| Feature/Solution | Autopack RFID Solutions | Barcode Scanning |
|---|---|---|
| Data Capture | Automated, real-time, bulk reading | Manual, one-by-one, line-of-sight required |
| Line of Sight | Not required | Required |
| Read Speed | Very high (hundreds of items simultaneously) | Low (single item at a time) |
| Accuracy | High (up to 98-99%) | Moderate (prone to human error) |
| Inventory Management | Dynamic, precise, real-time updates | Static, periodic, labor-intensive |
| Labor Efficiency | Extremely high (automation) | Low (manual scanning and data entry) |
| Error Rate | Very low (automated) | Moderate to High (manual processes) |
| Durability | Tags highly durable, resistant to environment | Barcodes can be easily damaged, smudged |
| Traceability | Excellent, end-to-end, granular | Good, but often limited to scanning points |
| Data Storage | High (can store more info) | Low (limited to numeric/alphanumeric code) |
| Security Features | Enhanced with unique IDs, anti-tamper options | Limited to visual inspection |
| Scalability | High (easily scalable to large operations) | Moderate (scaling requires more manual effort) |
| Cost of Ownership | Moderate to High (initial investment, lower ongoing) | Low (initial investment, higher ongoing labor) |
Brands






Contact us to find out more
Frequent Asked Questions on RFID
-
What is RFID?RFID stands for Radio-Frequency Identification. It’s an automatic identification technology that uses radio waves to wirelessly identify and track objects, animals, or people. An RFID system typically comprises RFID tags, an RFID reader, and an antenna, all connected to a host computer system.
-
How does RFID work at a fundamental level?An RFID reader emits radio waves to activate and communicate with RFID tags. When a tag enters the reader’s radio frequency field, it transmits its unique data back to the reader. The reader then converts these radio waves into digital data, which is sent to a computer system for processing, analysis, and integration with existing business applications.
-
What are the key components of an RFID system?The core components include: RFID Tag (Transponder): Consists of a microchip for data storage and an antenna for communication. RFID Reader (Interrogator): A device that transmits and receives radio signals to/from tags. Antenna: Facilitates the transmission and reception of radio waves between the reader and the tag. RFID Software/Middleware: Processes and manages the data collected from readers, integrating it with backend systems like ERP or WMS.
-
What are the different types of RFID tags and their primary uses?Passive RFID Tags: No internal power source; they draw power from the reader’s radio waves. They are inexpensive, small, and have a shorter read range (a few centimeters to ~15 meters). Ideal for inventory, asset tracking, and access control. Active RFID Tags: Have their own power source (battery). They offer a longer read range (up to 150 meters or more) and can transmit data continuously. Used for real-time locating systems (RTLS), vehicle tracking, and monitoring high-value assets. Semi-Passive (Battery-Assisted Passive – BAP) Tags: Have a battery to power the microchip but rely on the reader’s power for communication. They offer enhanced features like sensor integration and better read range than passive tags.
-
Is specialized hardware required for a barcode system?Yes, specialized hardware is typically required. This includes barcode scanners (which can be handheld, fixed-mount, or integrated into mobile computers) to read the barcodes, and barcode label printers to generate the physical labels. The specific type of hardware depends on the application and environment.
-
How does RFID compare to barcodes, and why might a business choose RFID?Refer to table above
-
What factors can affect RFID system performance, particularly around metal and liquids?Metal and liquids can significantly interfere with RFID signals, especially for UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) tags. Metal can reflect signals, creating dead spots, while liquids can absorb them. Proper tag selection (e.g., on-metal tags), antenna placement, and system calibration are crucial to mitigate these issues and ensure reliable performance in challenging environments.
-
What industries are currently leveraging RFID solutions effectively?Manufacturing: For WIP tracking, tool management, and quality control. Retail: For inventory accuracy, loss prevention, and omnichannel fulfillment. Logistics & Supply Chain: For real-time asset tracking, warehouse management, and end-to-end visibility. Healthcare: For tracking medical equipment, patient identification, and pharmaceutical management. Automotive: For component tracking, vehicle assembly, and parts management. Aerospace & Defense: For maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations and asset management.
-
What is the typical cost of an RFID solution for a business, and what drives these costs?The cost varies significantly based on scale, complexity, and components depending on operational needs. The whole solution would consist of Tags, Readers, Antennas, Printers/Encoders, Software & Integration, Installation & Services. Contact us for a consultation session to find out more
-
Can RFID solutions be integrated with existing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)?Absolutely. Integration with ERP and WMS is a critical aspect of modern RFID deployments. Middleware solutions are often used to act as a bridge between the RFID hardware (readers, tags) and the existing software infrastructure. This allows real-time RFID data (e.g., inventory updates, asset locations) to flow seamlessly into the ERP/WMS, automating processes, enhancing data accuracy, and providing a comprehensive view of operations.
-
What is the return on investment (ROI) typically seen from implementing RFID?The ROI for RFID solutions can be substantial and rapid, often achieved within 12-24 months. Businesses typically see returns through: Reduced Labor Costs: Automation of manual counting and tracking. Minimized Shrinkage/Losses: Improved accuracy and anti-theft capabilities. Optimized Inventory Levels: Reduced overstocking and fewer stockouts. Increased Productivity: Faster workflows and reduced downtime. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Better product availability and efficient service. Improved Compliance: Streamlined data for regulatory requirements.
-
How does Autopack ensure the quality and performance of its RFID solutions?Autopack focuses on providing robust and reliable RFID solutions. While specific details would be provided during a consultation, general practices for quality assurance in RFID solutions include: High-Quality Hardware: Sourcing durable and high-performing RFID tags, readers, and antennas. Autopack is the platinum partner for Zebra, a leading brand in the AIDC. Optimized Software: Developing or integrating with best-in-class software solutions for data processing and management. Expert System Design: Employing experienced engineers to design optimal reader placement and system architecture. Rigorous Testing: Conducting comprehensive testing, including pilot programs, to ensure system accuracy and reliability in real-world conditions. Ongoing Support and Maintenance: Providing continuous technical support, preventive maintenance, and system optimization services to ensure long-term performance.